What is the Maximum Formable Thickness for Thermoforming?
What is the Maximum Formable Thickness for Thermoforming? Thermoforming is a process that shapes plastic materials by heating them to a pliable temperature and then forming them over a mold. The maximum formable thickness of a material for thermoforming depends on several factors, including the machine’s specifications and the type of plastic used. For INPAK thermoforming machines, the maximum thickness of the material that can be shaped typically ranges between 0.15 mm to 1.5 mm. This range ensures that the material can be heated evenly and can be manipulated easily without compromising its structural integrity. As a result, INPAK machines are optimized for handling a wide variety of plastics within this thickness range, allowing for the creation of diverse products.
Table of Contents
The thickness of the material directly impacts how it will behave during the forming process. Thicker materials generally require more heat to achieve the desired flexibility, while thinner materials heat faster and require less energy. With INPAK’s advanced heating systems, these challenges are mitigated, ensuring consistent results regardless of material thickness. However, beyond 1.5 mm, the material may not form correctly, as the heating and stretching may lead to issues like warping or cracking, making the process less efficient.
The maximum formable thickness also influences the final product’s strength, appearance, and overall quality. For example, thinner materials are often used in packaging or products where flexibility and clarity are essential. On the other hand, thicker materials are more suitable for products that require additional durability, such as automotive parts or industrial components. Therefore, selecting the right thickness for the intended application is crucial to achieving the best possible outcome in thermoforming. What is the Maximum Formable Thickness for Thermoforming?
What is the Maximum Thickness for Thermoforming?
The maximum thickness for thermoforming varies depending on the machine capabilities and the type of plastic being used. In the case of INPAK Thermoforming machines, the maximum thickness typically falls within the range of 0.15 mm to 1.5 mm. This range covers the most common materials used in thermoforming, such as polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and others. The ability to handle this range of thicknesses allows INPAK machines to cater to a wide range of industries, from packaging to automotive.
Thermoforming thicker materials presents several challenges. The main issue with using thicker plastics is ensuring uniform heating across the entire sheet. The thicker the material, the more difficult it is to maintain a consistent temperature throughout. INPAK overcomes this with advanced temperature control and heating systems that ensure even heating, allowing the material to be shaped without issues. However, as the material thickness increases beyond 1.5 mm, achieving optimal results becomes more difficult, and additional considerations such as custom molds and slower processing speeds may be necessary.
The optimal thickness for thermoforming is also influenced by the final product’s requirements. For example, products requiring high impact resistance, such as automotive parts, may need thicker materials, while packaging applications typically use thinner materials for cost efficiency and ease of handling. As a result, choosing the right thickness is essential not just for the forming process, but also for the product’s performance and cost-effectiveness in production.
Which Material Thickness is Suitable for Which Products?
The selection of material thickness in thermoforming is crucial for determining the final product’s functionality and appearance. Thinner materials are generally used for applications where flexibility, transparency, and ease of handling are essential. Products such as blister packs, trays, and food packaging are typically made from materials that range from 0.15 mm to 0.6 mm thick. These materials can be easily formed and provide the necessary durability for lightweight applications without adding unnecessary weight or cost to the product.
On the other hand, thicker materials are used for products that require greater strength and impact resistance. For instance, materials with thicknesses between 0.6 mm and 1.5 mm are commonly used for creating automotive parts, industrial components, and heavy-duty packaging. These materials can withstand higher stresses and provide the rigidity necessary for such applications. The increased thickness also allows for better insulation and protection, making them suitable for products that must endure harsh environments or handling conditions.
Choosing the right material thickness is also influenced by the intended use of the product. Products that need to be visually appealing, such as cosmetic packaging or point-of-sale displays, may benefit from thinner materials that allow for more intricate designs and better surface quality. In contrast, products that will undergo significant wear and tear, like protective covers and heavy-duty trays, require thicker materials to ensure longevity and durability. The thickness must therefore match the functional requirements of the product to achieve the best performance.
Minimum and Maximum Thickness Limits in Thermoformed Plastics
The minimum and maximum thickness limits in thermoformed plastics are essential considerations when selecting materials for production. On the lower end, the minimum thickness is usually around 0.15 mm, as this ensures the material can be effectively heated and shaped without tearing or losing structural integrity. Thin plastics are suitable for high-volume production where flexibility and low cost are critical factors. However, working with such thin materials requires precision to avoid issues such as wrinkling, distortion, or incomplete forming.
At the upper end, the maximum thickness for thermoforming generally ranges up to 1.5 mm. Beyond this limit, the process becomes increasingly difficult and may lead to uneven heating, which can result in defects such as warping or cracking. INPAK’s thermoforming machines are designed to handle this range of thicknesses, but as the material thickness increases, additional steps or modifications, such as using special heating controls or slower processing speeds, may be required to ensure optimal results. This ensures that even thicker materials can be successfully thermoformed, although the range of applications becomes more specialized.
Understanding the minimum and maximum thickness limits is essential for selecting the right material for a particular application. For lighter, flexible products, thinner materials are preferable, while thicker materials are necessary for items that need greater strength and durability. Manufacturers must consider both the capabilities of their thermoforming equipment and the specific requirements of the final product to determine the best material thickness for their production needs.
The Impact of Thermoform Thickness on Cost and Production Process
The thickness of the material used in thermoforming has a significant impact on both the cost and the production process. Thinner materials generally lead to lower material costs, as less plastic is used per unit of production. Additionally, thinner materials are easier to heat and form, which can reduce cycle times and improve overall efficiency in the production process. This can lead to cost savings, especially in high-volume production runs where speed and cost are paramount considerations.
However, using thicker materials increases both material and processing costs. Thicker plastics require more energy to heat, and the increased material costs add to the overall expense. Furthermore, thicker materials often require slower processing times to ensure even heating and proper forming, which can reduce the speed of production. In some cases, specialized equipment or molds may be needed to handle thicker materials, further increasing production costs. This trade-off must be considered when deciding on material thickness, as it will directly affect the cost-efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Choosing the right material thickness is crucial for balancing cost and production efficiency. For applications where high durability and strength are necessary, thicker materials may be the best choice, despite the higher cost. However, for lightweight, flexible products, thinner materials may provide the desired performance at a lower cost, making them more suitable for cost-sensitive applications. Manufacturers must weigh the trade-offs between material thickness, production costs, and the final product’s functional requirements to achieve the best results.
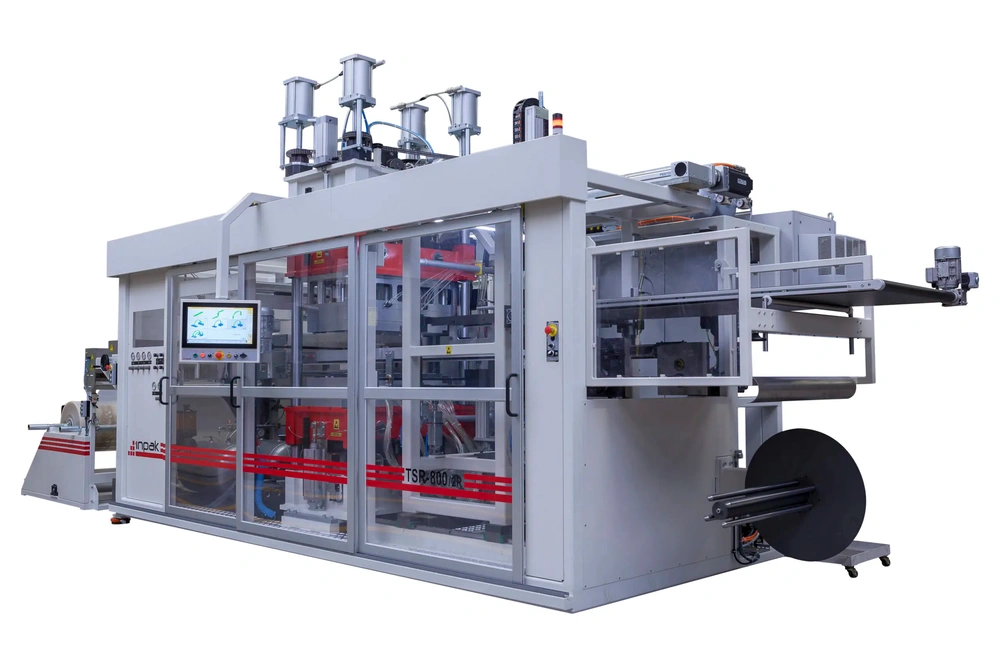
Thermoforming Machine Options for Formable Products by INPAK
INPAK thermoforming machines are designed to handle a wide range of plastic materials within the thickness range of 0.15 mm to 1.5 mm. These machines are equipped with advanced heating, forming, and cutting technologies, making them versatile and adaptable to different types of products. Whether producing lightweight packaging or more robust industrial components, INPAK’s machines offer flexible options that cater to the specific needs of each application.
For thinner materials, INPAK machines provide fast heating and precise forming capabilities, ensuring that products are shaped quickly and with minimal defects. These machines are ideal for producing items like trays, blister packs, and other packaging products where speed and cost-efficiency are crucial. For thicker materials, INPAK machines offer enhanced control over heating and forming processes, allowing for the production of more durable and complex products like automotive parts and heavy-duty containers. This flexibility ensures that manufacturers can produce a wide variety of thermoformed products while maintaining high standards of quality.
In addition to handling different material thicknesses, INPAK offers various customization options to optimize the thermoforming process for specific products. These options include adjustable heating control systems, customizable molds, and specialized forming techniques to achieve the desired product characteristics. Whether producing simple packaging or intricate industrial parts, INPAK’s thermoforming machines are capable of delivering high-quality results across a broad spectrum of applications.