Thermoformable Materials: PET, CPET, PP, PS, OPS, PLA
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process that uses heat to mold plastic materials into specific shapes. The materials used in thermoforming must be capable of becoming pliable under heat and retaining their shape once cooled. Some of the most commonly used thermoformable materials include Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Crystallized Polyethylene Terephthalate (CPET), Polypropylene (PP), Polystyrene (PS), Oriented Polystyrene (OPS), and Polylactic Acid (PLA). Each of these materials has unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications, ranging from packaging to medical and consumer products.
Table of Contents
PET is widely known for its excellent clarity, strength, and recyclability. It is often used in packaging applications like beverage bottles and food containers. CPET, a crystallized form of PET, is more heat resistant and is commonly used in food trays that require high-temperature resistance during microwave heating. Polypropylene, on the other hand, is a versatile thermoplastic used in food containers, automotive parts, and consumer goods. Polystyrene, both in its solid and foamed forms, is employed in a variety of disposable products and insulation materials. OPS, which is oriented polystyrene, provides increased strength and clarity, making it ideal for transparent food packaging. PLA, a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources, is increasingly popular in eco-friendly packaging and disposable products.
These materials are selected based on their specific advantages and the requirements of the product being made. Whether for food packaging, medical applications, or consumer goods, the Thermoforming machines process allows manufacturers to create a variety of products efficiently. The right choice of material can enhance the durability, transparency, and sustainability of the final product, making thermoforming a highly adaptable and valuable manufacturing technique.
What is Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)? What Are Its Advantages?
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a type of polyester made from the polymerization of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. It is one of the most widely used thermoplastics, particularly in the production of containers, packaging, and textiles. PET is known for its exceptional combination of properties, which include excellent strength, chemical resistance, and impact resistance. These qualities make it a popular choice for packaging materials that need to withstand physical stress while maintaining clarity.
One of the key advantages of PET is its high degree of recyclability. PET bottles and containers can be recycled into new products, contributing to its sustainability. The material is lightweight, yet strong, which reduces transportation costs and energy consumption during logistics. PET’s resistance to moisture, oils, and solvents also makes it ideal for packaging food and beverages, as it helps preserve the freshness of the product inside. Additionally, PET is cost-effective to produce, which makes it an affordable choice for manufacturers.
In terms of performance, PET is highly versatile and can be molded into various forms, including rigid, flexible, and transparent materials. This adaptability has allowed PET to be used in a wide range of applications, from bottled beverages to medical equipment. Its transparency is another desirable feature, as it allows consumers to see the contents of the packaging. Overall, PET’s strength, recyclability, and versatility make it a top choice for thermoforming processes in industries ranging from food packaging to consumer goods.
Characteristics and Applications of Crystallized Polyethylene Terephthalate (CPET)
Crystallized Polyethylene Terephthalate (CPET) is a modified version of PET that has undergone a crystallization process to enhance its heat resistance. Unlike standard PET, CPET can withstand higher temperatures, which makes it ideal for applications that require the material to endure heat without deforming. This characteristic is particularly important in the food industry, where CPET is commonly used for manufacturing microwaveable food trays and containers. CPET’s ability to maintain its shape and strength at high temperatures allows for easy handling and the retention of its structural integrity when used in environments like ovens or microwaves.
CPET also exhibits improved chemical resistance compared to standard PET, making it a durable option for products that need to resist various substances. The crystallization process increases the material’s rigidity, which is beneficial for items that require more structural support. Additionally, CPET maintains excellent impact resistance and can be molded into precise shapes, making it an ideal material for packaging and manufacturing. CPET’s performance in high-temperature applications has made it a go-to material for food packaging that requires both strength and heat resistance.
Another advantage of CPET is its ability to be recycled, much like PET, making it an environmentally friendly option for packaging. Its excellent dimensional stability ensures that it retains its shape even after exposure to high heat, which is particularly beneficial for the food industry. As consumer demand for microwaveable meals increases, CPET continues to gain traction as a reliable, sustainable, and heat-resistant material for packaging. Its ability to balance durability with heat tolerance positions it as a key player in the thermoforming industry.
What is Polypropylene (PP)? Thermoforming Applications
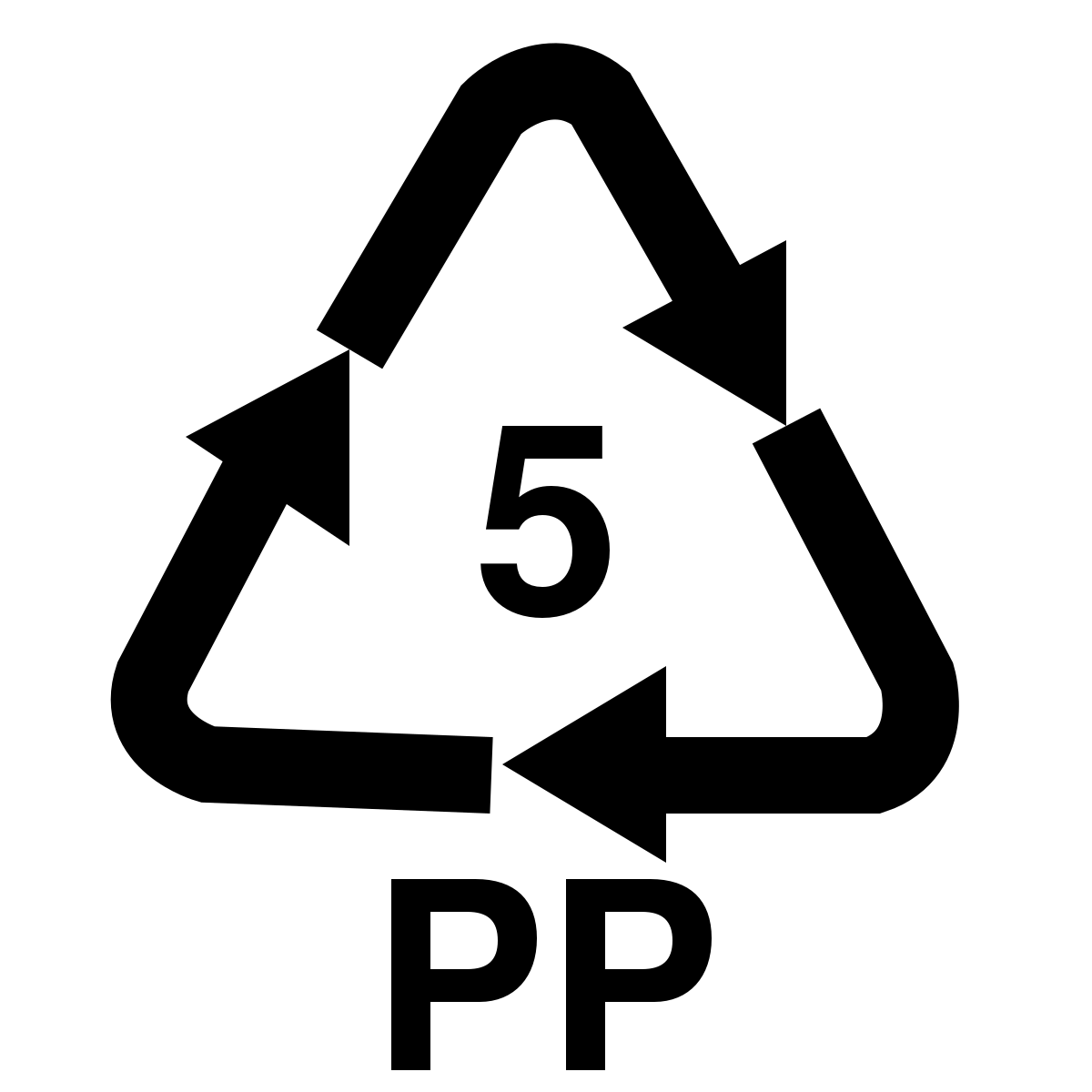
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer known for its flexibility, resistance to fatigue, and high melting point. These properties make PP an ideal choice for a wide range of thermoforming applications, particularly in the production of food packaging, automotive components, and consumer products. PP is lightweight, yet it offers excellent strength and rigidity, which is why it is often used in applications that require both durability and cost-effectiveness. Its low density also makes it an efficient material for reducing overall production and shipping costs.
In thermoforming, PP is commonly used for manufacturing containers, trays, and lids for food packaging. It is resistant to grease, oils, and chemicals, making it suitable for packaging products like frozen foods and snacks. PP’s ability to retain its shape after heating and cooling also makes it an excellent material for producing durable and long-lasting items. In addition, PP can be used in the automotive industry to create interior components, such as dashboards and door panels, thanks to its high strength and resistance to wear and tear.
Polypropylene also boasts good thermal resistance, which makes it useful for producing products that will be exposed to varying temperature conditions. Its flexibility in terms of molding and shaping allows for the creation of intricate designs, which is why it is widely used in consumer products such as household goods, furniture, and packaging. The material’s cost-effectiveness and versatility continue to make it one of the most widely used thermoplastics in various manufacturing processes, including thermoforming.
What is Polystyrene (PS)?
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene. It is one of the most commonly used thermoplastics due to its ease of processing and relatively low cost. PS is available in both solid and foamed forms, each of which has distinct properties and applications. In its solid form, PS is a hard, brittle plastic with a high degree of transparency, making it ideal for products like CD cases, plastic cups, and food containers. In its foamed state, it becomes lightweight and insulating, making it popular in packaging materials and insulation products.
PS is particularly known for its clarity and ease of molding, which allows it to be used in a variety of consumer and industrial applications. However, it has limitations in terms of impact resistance, as it can be brittle and prone to cracking under stress. This makes it less suitable for applications where durability is a critical factor. Despite this, its low cost and wide availability make it a popular choice for disposable products like cutlery, food containers, and packaging materials.
In the thermoforming industry, PS is typically used for creating lightweight, transparent products. Its ease of processing allows manufacturers to quickly produce a variety of products, including packaging and household items. While PS is not as durable as some other thermoplastics, its versatility and affordability continue to make it a go-to material for many everyday applications.
What is Oriented Polystyrene (OPS) and Where is It Used?
Oriented Polystyrene (OPS) is a type of polystyrene that has been mechanically stretched, causing its molecular structure to align in a specific direction. This process improves the material’s strength, rigidity, and transparency compared to regular polystyrene. OPS is often used in packaging applications where clarity and durability are important. It is most commonly found in food packaging, such as trays, clamshells, and containers, where visibility of the product is essential.
OPS offers superior strength compared to standard polystyrene, which allows it to maintain its shape during handling and transportation. Its enhanced transparency makes it a preferred choice for food packaging, as it allows consumers to easily view the product inside. OPS is also more resistant to cracking and breakage, which adds to its appeal for packaging that needs to endure stress during transit and use. The material is lightweight yet durable, making it ideal for cost-effective packaging solutions that do not compromise on quality.
Another notable feature of OPS is its excellent thermoforming characteristics. The material can be easily molded into complex shapes, providing manufacturers with flexibility in design. OPS is also widely used in display products, such as sign holders and point-of-purchase displays, due to its clarity and rigidity. Its ability to combine strength with visual appeal makes it a valuable material in the packaging and consumer product industries.
What is PLA Plastic and Where is It Used?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic polymer made from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. PLA is one of the most popular alternatives to petroleum-based plastics, particularly due to its environmental benefits. Unlike conventional plastics, PLA decomposes naturally in composting environments, making it an attractive option for eco-friendly products. PLA is widely used in packaging, particularly in the food and beverage industry, where it is used for creating disposable cutlery, cups, and containers.
PLA’s properties include good transparency, rigidity, and ease of processing, making it a versatile material for thermoforming applications. It is commonly used for producing biodegradable packaging materials that are both lightweight and durable. PLA is also used in the production of textiles, medical implants, and agricultural films. However, PLA has limitations in terms of heat resistance, which restricts its use in applications that require exposure to high temperatures.
Despite these limitations, PLA’s biodegradable nature has led to its increased use in environmentally conscious manufacturing. The material is an ideal choice for single-use products like food containers, as it provides a more sustainable alternative to traditional plastics. PLA’s popularity is expected to grow as demand for sustainable products continues to rise, and its use in the thermoforming process provides an opportunity for manufacturers to meet the needs of eco-conscious consumers.
Heat Resistance and Application Effects of Thermoforming Machines
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process that relies on heating plastic materials to their softening point, where they become pliable and can be molded into desired shapes. The heat resistance of both the material and the Thermoforming machines plays a significant role in determining the quality of the final product. Materials with higher heat resistance, such as CPET and PP, are suitable for applications where the product will be exposed to high temperatures, such as food trays and packaging that need to withstand microwave or oven heating.
Thermoforming machines must be designed with precision temperature controls to ensure uniform heating of the material. These machines are equipped with heating elements that gradually raise the temperature of the plastic to its forming point, ensuring it reaches the optimal state for molding. The use of high-quality thermoforming machines ensures that the material can be shaped consistently, minimizing defects and improving the overall efficiency of production. The ability to control heat is also critical for minimizing waste and optimizing the production cycle.
The application effects of thermoforming machines vary based on the material being used and the complexity of the product being manufactured. Materials with lower heat resistance, such as PS, may require less heat to form, but they also tend to be more prone to deformation at higher temperatures. In contrast, materials like CPET offer greater heat resistance, which is ideal for products that require exposure to elevated temperatures. Advanced thermoforming machines are capable of handling a wide range of materials with varying heat resistance, ensuring the production of high-quality products across various industries.
How Are Plastics Produced with Thermoforming Machines?
Thermoforming is a process that transforms plastic sheets or films into three-dimensional shapes by applying heat and pressure. In the first step, a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable state in a heating chamber. Once the plastic reaches the desired temperature, it is transferred to a molding station where it is formed into a mold. The mold can be designed to create any number of shapes, from simple trays and containers to complex, intricate designs for medical or automotive products.
The Thermoforming machines typically uses either vacuum or pressure to mold the plastic sheet against the contours of the mold. Vacuum forming uses a vacuum to suck the heated plastic sheet into the mold, while pressure forming uses air pressure to force the plastic into the mold. The plastic then cools and solidifies, retaining the shape of the mold. After the cooling process, the formed plastic is removed from the mold and trimmed to the desired dimensions.
Thermoforming machines are highly versatile and can accommodate a variety of plastic materials, such as PET, PP, PS, and PLA. The process can be adapted to produce products in a wide range of sizes and complexities, from packaging materials to consumer goods and medical devices. By utilizing precise control over temperature and pressure, thermoforming machines ensure high-quality, consistent products, making this process ideal for large-scale production runs.
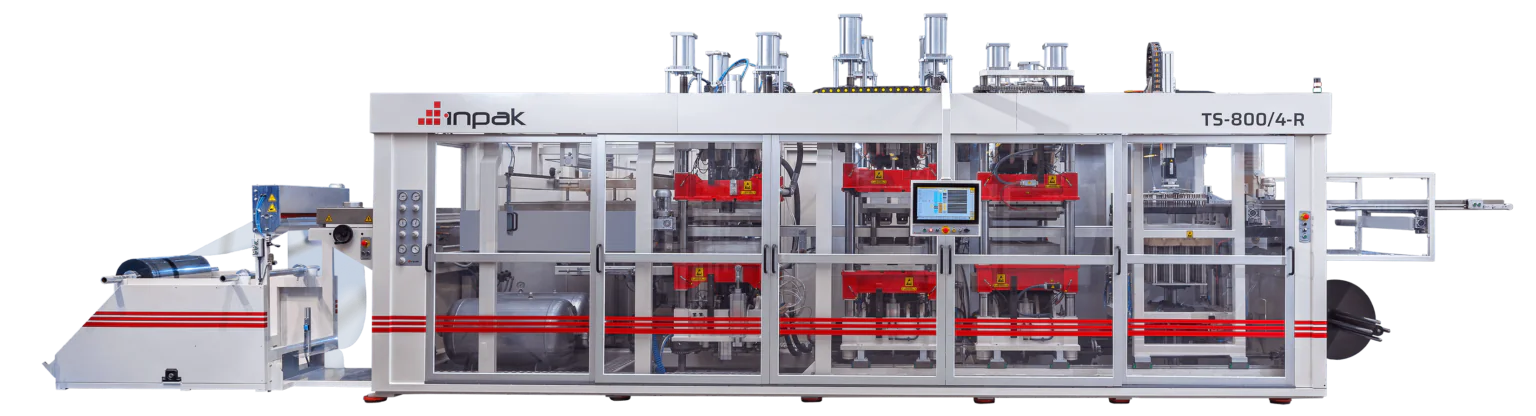
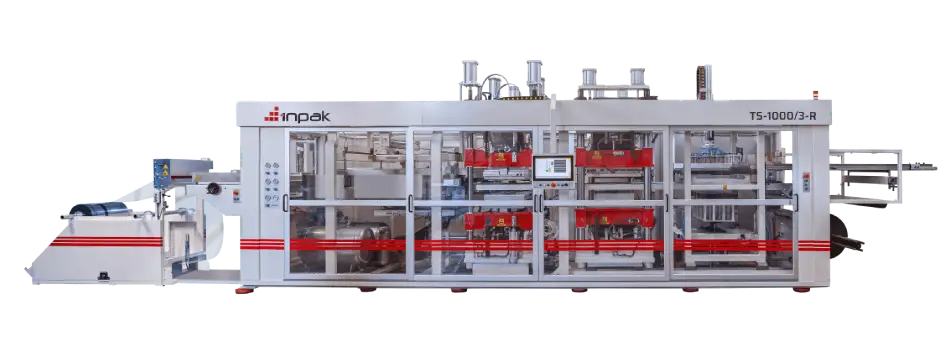
Thermoforming Machines for Plastic Packaging Production by INPAK
INPAK specializes in producing thermoforming machines designed for high-volume plastic packaging production. These machines are known for their efficiency, precision, and flexibility. INPAK’s thermoforming machines are engineered to handle a variety of materials, including PET, CPET, PP, and PLA, making them suitable for diverse packaging applications, from food containers to medical packaging. The machines are designed to deliver fast production cycles while maintaining high-quality standards in the final product.
INPAK’s machines are equipped with advanced features such as temperature control systems, vacuum and pressure forming capabilities, and customizable mold options. These features enable manufacturers to produce products with complex shapes and high precision. The machines are also designed with energy efficiency in mind, ensuring that production runs are cost-effective and sustainable. INPAK’s commitment to innovation ensures that its thermoforming machines meet the evolving demands of the packaging industry, offering solutions for both standard and specialized applications.
By investing in INPAK thermoforming machines, manufacturers gain access to state-of-the-art technology that streamlines the production process, reduces waste, and ensures consistency in the quality of the final product. INPAK’s machines provide an excellent option for companies looking to enhance their packaging operations while maintaining flexibility, speed, and sustainability in their production lines.